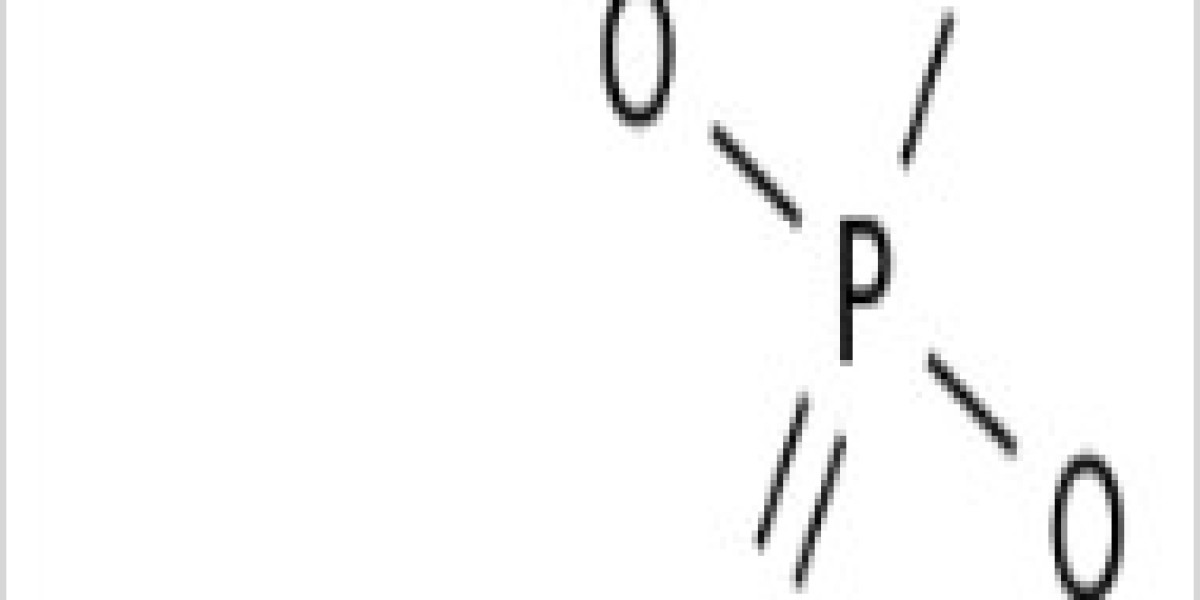
Alum (aluminum phosphate formula and aluminum hydroxide) is a widely used adjuvant for over a century that targets the innate immune system for activation through various mechanisms, including serving as antigen depot, targeting the antigen to DCs, and induction of inflammation, altogether culminating in the generation of acquired cellular, Th1 and Th2, and humoral immune responses.
The morphology of aluminum hydroxide adjuvant and aluminum phosphate formula adjuvant provides a mechanism that uniformly distributes microgram quantities of antigen onto milligram quantities of adjuvant. As seen in Figure 5-1, the functioning unit of both adjuvants is an aggregate ranging in size from 2 to 20 μm composed of the nanometer sized primary particles. The distribution of alpha casein, bovine serum albumin and anthrax recombinant protective antigen in monovalent and combination vaccines containing aluminum hydroxide adjuvant was studied by fluorescence microscopy.
In order to attract the attention of the immune system and build an immune response, most vaccines require the addition of an adjuvant. Aluminum salts such as aluminum hydroxide, aluminum phosphate formula and aluminum potassium sulfate have been used safely in vaccines for more than 70 years. A recently developed adjuvant suspension used with the Shingrix vaccine is ASO1B. AS01B is made of up of monophosphoryl lipid A (MPL), an immune-boosting substance isolated from the surface of bacteria, and QS-21, a natural compound extracted from the Chilean soapbark tree. Adjuvants have to be carefully used and manufactured since they can lead to severe inflammation. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not currently approve the use of pure adjuvants outside of a vaccine.
Aluminum-containing adjuvants have historically served as immunostimulants in vaccines and continue to be the most widely used adjuvants. Several aluminum compounds are used and are known as aluminum hydroxide, aluminum phosphate formula and alum. All three of these commonly used names are scientific misnomers. Although this family of adjuvants has been used the longest, it is only recently that we have begun to understand their mechanism of action and the complexity of formulating them with antigens.
Aluminum phosphate formula adjuvant is a chemically amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate in which some of the hydroxyl groups of aluminum hydroxide are replaced by phosphate groups. The disordered, amorphous state is responsible for the high surface area and high adsorptive capacity.
The surface of aluminum phosphate formula adjuvant is composed of Al-OH and Al-OPO3 groups. The IEP varies from 9.4 to 4.5 depending on the degree of phosphate substitution.19 Commercial aluminum phosphate formula adjuvants have IEP values in the 4.5 to 5.5 range. In contrast with aluminum oxyhydroxide, commercial aluminum phosphate formula adjuvants are negatively charged at pH 7.4
The earliest vaccines containing aluminum adjuvants were prepared by in situ precipitation. A solution of alum was mixed with a solution of the antigen dissolved in a phosphate buffer. It is common practice to refer to the adjuvant produced by in situ precipitation as alum. The precipitate is amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate and has similar composition and properties as aluminum phosphate formula adjuvant.17,20
The techniques that can be used to characterize aluminum-containing adjuvants have been reviewed by White and Hem.